When managing or living in a House in Multiple Occupation (HMO), safety is always a top priority. One of the most essential safety features in any HMO is the fire door. Fire doors are not just a recommendation—they are a legal requirement under UK law. In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about HMO fire door regulations, including what they are, why they matter, and how to ensure compliance.
Contents
What Are HMO Fire Door Regulations?
HMO fire door regulations are legal guidelines set out to ensure that landlords of shared properties install and maintain fire-resistant doors. These regulations are part of broader fire safety laws aimed at protecting tenants in HMOs, where the risk of fire is higher due to the shared nature of the living space.
Fire doors are specifically designed to withstand fire for a certain amount of time—typically 30 or 60 minutes—giving residents enough time to evacuate safely and helping to contain the fire within a particular area of the house.
Why Are Fire Doors Crucial in HMOs?
Here are some key reasons why fire doors are critical in any HMO setting:
- Higher fire risk: With multiple tenants using kitchens, electrical appliances, and heaters, the chances of a fire starting are significantly increased.
- Shared escape routes: Unlike single-family homes, HMOs usually have shared hallways and staircases. Fire doors help keep these routes clear and safe during emergencies.
- Legal responsibility: Landlords are legally responsible for the safety of their tenants. Not having proper fire doors in place could lead to serious consequences, including fines or imprisonment.
Key Requirements for HMO Fire Doors
Understanding the specific requirements can help landlords avoid penalties and keep their tenants safe. Below are the primary regulations that must be followed:
1. Fire-Resistant Materials
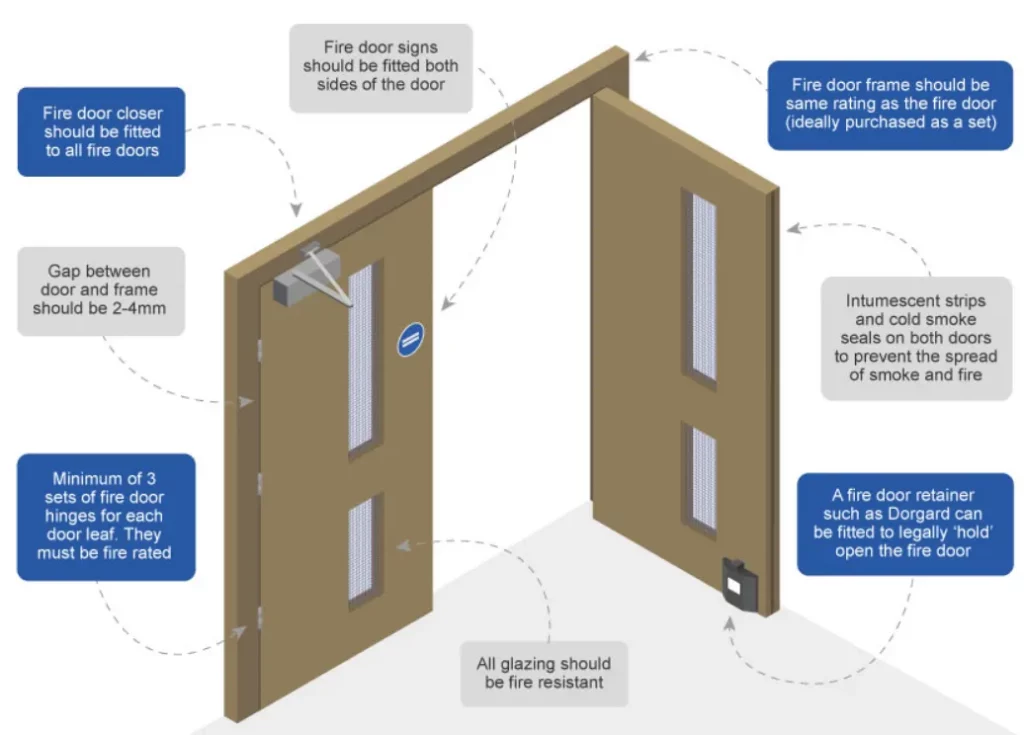
Fire doors must be FD30-rated as a minimum, meaning they can withstand fire for at least 30 minutes. In higher-risk HMOs, FD60-rated doors may be required.
2. Self-Closing Mechanisms
All fire doors must be fitted with a self-closing device. This ensures the door automatically shuts after being opened, which is crucial for containing fires.
3. Smoke Seals and Intumescent Strips
Fire doors should be equipped with smoke seals and intumescent strips around the edges. These expand in the heat of a fire to seal gaps and prevent smoke from spreading.
4. Proper Fitting and Maintenance
Even a certified fire door can fail if it’s not installed correctly. Doors should be installed by qualified professionals and regularly inspected for:
- Warping or damage
- Faulty hinges or closers
- Gaps that exceed 3mm between the door and frame
Locations Where Fire Doors Are Required in HMOs
Fire doors should be strategically placed throughout the HMO to protect escape routes and high-risk areas. These typically include:
- Bedrooms (especially in larger HMOs)
- Kitchens
- Living rooms or communal areas
- Corridors leading to exits
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to comply with fire door regulations in an HMO can result in severe penalties:
Legal action: Councils have the authority to prosecute non-compliant landlords under the Housing Act 2004.
Fines and imprisonment: Landlords may face unlimited fines or up to two years in prison for serious breaches.
Invalid insurance: If a fire occurs and the property is found to be non-compliant, your insurance could be voided, leading to enormous financial losses.
How to Ensure You’re Compliant
If you’re unsure whether your HMO meets the current fire safety standards, the best step is to conduct a professional fire risk assessment. Many letting agents and fire safety companies offer this service, helping landlords identify weak points and take action before a problem occurs.
Final Thoughts
Understanding and following HMO fire door regulations is not just about meeting legal standards—it’s about protecting lives. As a landlord, it’s your duty to ensure your tenants are safe in the event of a fire. By installing certified fire doors, keeping them in good condition, and staying informed of your legal obligations, you can create a safer and more compliant property.